VET CELL TECH
Stem Cells

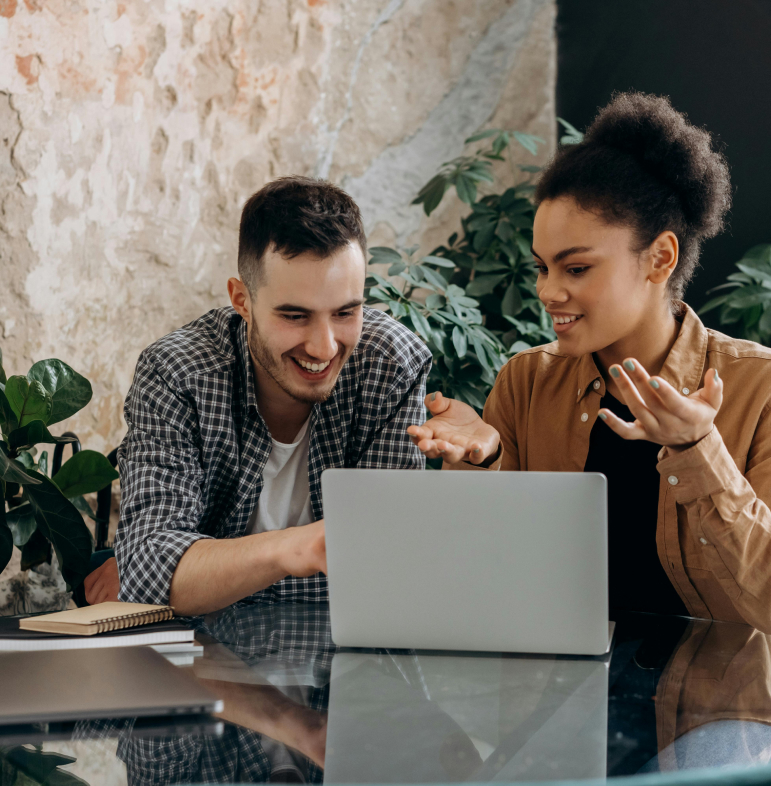
Stem cells are cells without which the animal body could not come into being and function. Animal embryo at the earliest stage of development consists only of stem cells. Their characteristic feature is that they have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into other types of cells in an almost unlimited manner. It is this trait that makes them valuable in the scientific and medical fields – stem cells give rise to all the cell types that make up the body.
Main type of stem cells used in veterinary medicine are mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). MSCs are a heterogeneous population of multipotent stem cells characterized by specific properties i.e. the ability to initiate the process of creating progenitor cells aimed at differentiation towards a specific cell line – osteogenic, chondrogenic and adipogenic. Moreover, MSCs are involved in the regeneration of damaged tissue in which they reside through paracrine and immunomodulatory modes. Cells with MSCs characteristics can be isolated from many organs and tissues of the animal body, but the majority of research and development is being conducted on bone marrow, umbilical cord or adipose tissue derived cells.
The beneficial effects of stem cells/MSCs in different autoimmune diseases are well-known and documented in numerous clinical trials and experiments, both in-vitro and in-vivo. Until recently, most therapies were based on autological stem cells – meaning that the donor and recipient are the same person. There have been attempts at developing drugs based on allogeneic stem cells/MSCs, meaning that the donor and the recipient are not the same. However, this approach still requires numerous donors and presents numerous challenges associated with the production process such as scalability, cost-effectiveness and product homogeneity.
These challenges can be overcome by using the new method of obtaining immortal and infinitely scalable pluripotent stem cells. This technology has been developed by Professor Shinya Yamanaka of Kyoto University who won the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine. He discovered that mature cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) very similar/almost identical to embryonic stem cells called induced PSCs (iPSCs), which can differentiate into any type of cell by appropriate external factors. This breakthrough was a game-changer for innovative stem cell based drugs and their production.
VET CELL TECH uses the iPSC technology in its production process as shown on the diagram below.
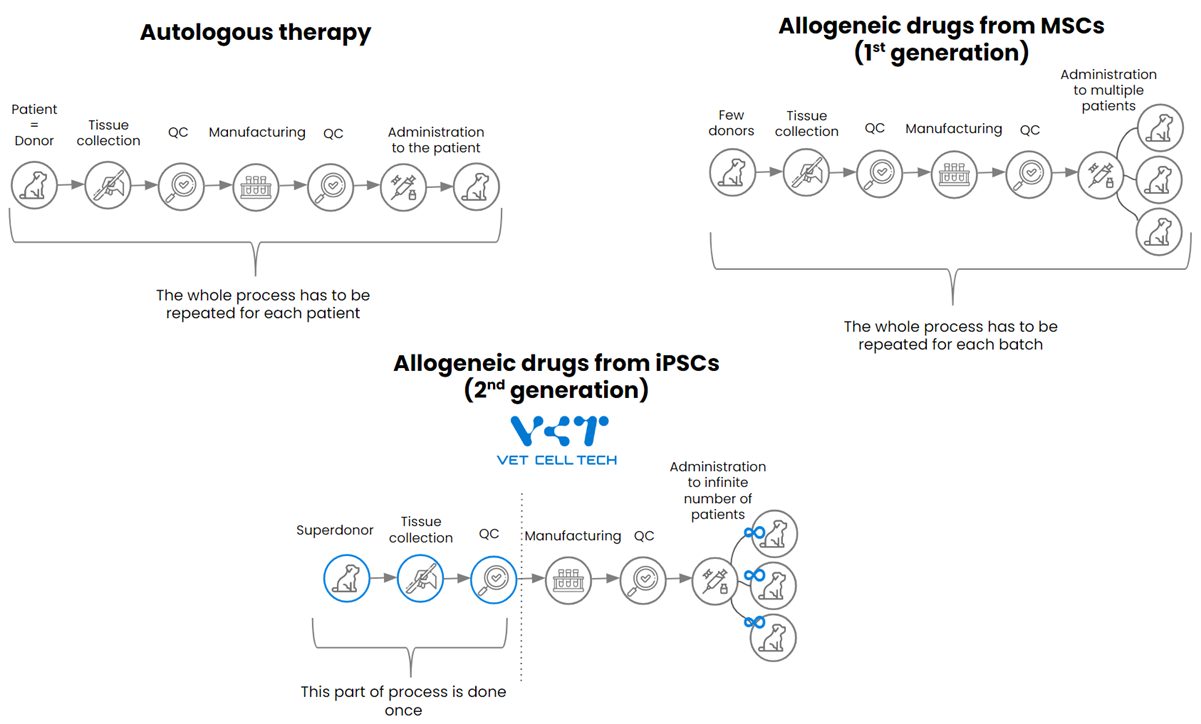

The main benefits of using iPSCs technology in cell – based drugs include primarily:
- possibility of selecting one superdonor with most potent cells
- homogeneous standard of end product in terms of quality, efficacy and safety
- simplified supply chain
- cost effectiveness
The iPSCs technology allows homogeneous/standardized end product in the manufacturing at scale, assuring unparalleled efficacy and safety as compared to allogeneic drugs which are coming from different donors from one batch to another. Due to shortened manufacturing processes associated with only one time material collection from a single superdonor, there is a significant transport reduction and supply chain simplification resulting in cost effectiveness.
The main differences between different technologies:
| Autologous stem cell therapy | Allogeneic stem cell drugs from MSCs | Allogeneic stem cell drugs from iPSC | |
| Final product | MSCs | MSCs | MSCs, iMSCs or others |
| Productisation | Therapy (service) | Drug (product) | Drug (product) |
| Donors | Multiple donors (each patient is its own donor) | Multiple donors (several per one batch) | One super donor |
| Source | MSCs derived from patients own tissue (most often adipose tissue) | MSCs derived from multiple donors each time when the new batch is being produced | iPSCs masterbank |
| Potency, efficacy, safety | Depends on donors cells, varies with each donor | Depends on donors cells, varies from one batch to another | High and uniform, based on superdonors cells |
| Supply chain and transport | Collection of patient’s own tissue, transport to manufacturing site and back | Regular collection and transport of the tissue from the veterinary clinics for each batch, with the need of sterility test of the donor material | No need for special supply chain, the whole process takes place at the manufacturing site |
| Material source collection | With each patient need to collect the tissue | With each production batch, need to collect the tissue | Only once |
| Homogeneity | Each patient will differ | Batches vary depending on donors | Constant, all batches are exactly the same |


